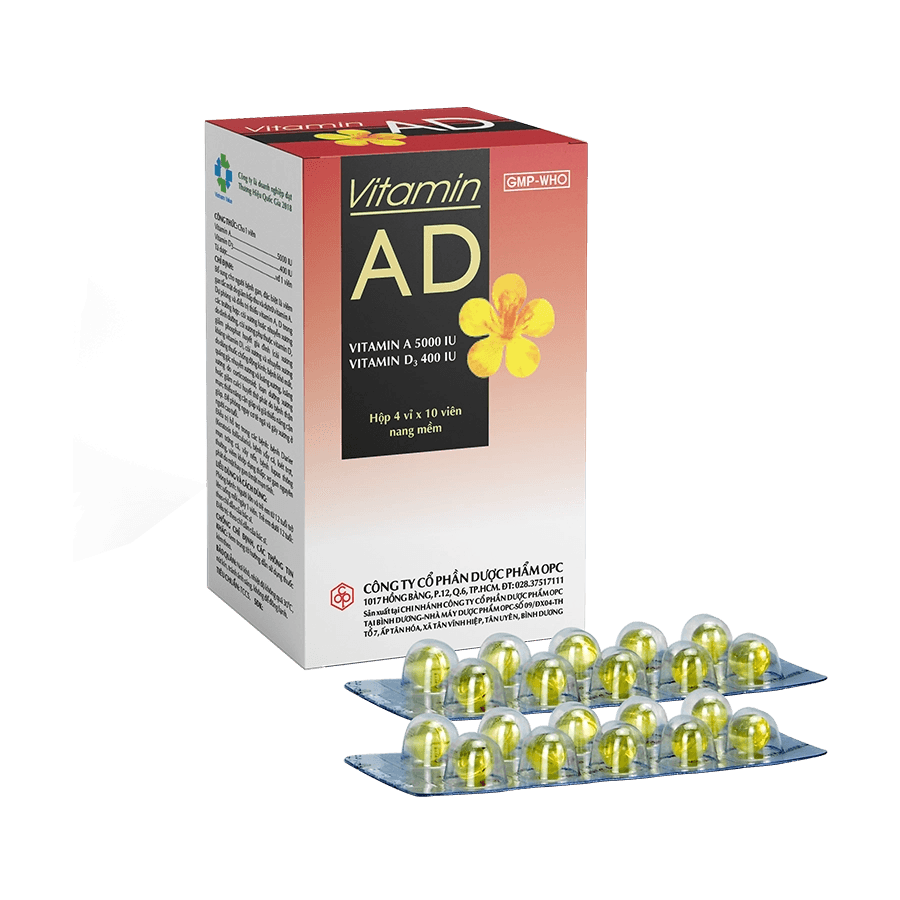
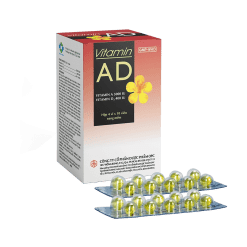
VITAMIN AD
FORMULA:
Vitamin A 5000 IU
Vitamin D3 400 IU
Excipients (Soya oil, gelatin, glycerol, propyl paraben) s.q.f 1 soft-gel
PHARMACODYNAMICS:
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for vision, growth and the development and maintenance of the epithelium.
In active form (1,25 – dihydroxycolecalciferol), vitamin D3 (or colecalciferol) together with parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate blood calcium levels. The main biological function of vitamin D is to maintain normal blood levels of calcium and phosphorus by increasing the efficiency of absorption of minerals from the diet, in the small intestine and by increasing the mobilization of calcium and phosphorus from the bones into the blood. Active forms of vitamin D3 may have a negative feedback effect on the formation of parathyroid hormone (PTH).
PHARMACOKINETICS:
Vitamin A (Retinyl Palmitate) is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract in the form of retinol (after being hydrolyzed by pancreatic enzymes). Fat malabsorption, protein deficiency, liver dysfunction or pancreatic dysfunctions reduces the absorption of vitamin A. Some retinols are stored in the liver and are released into the blood in the form associated with a specific globulin. The body’s vitamin A reserves usually meet your body’s needs for several months. The free retinol is conjugated with glucuronic and is oxidized to retinal and retinoic acid and then is excreted in the urine and faeces with other metabolites.
Vitamin D3 is well absorbed from the small intestine. Approximately 80% of oral vitamin D3 is concentrated in the chyle and is absorbed by the lymphatic system. Vitamin D3 and its metabolites circulate in the blood, associate with specific alpha globulins. The plasma half-life of vitamin D3 is 19-25 hours, but the drug is stored for long periods in adipose tissue.
Vitamin D3 and its metabolites are mainly excreted via bile and feces, only a small amount appears in the urine. Vitamin D3 can be secreted into the milk.
INDICATIONS:
Supplement vitamin A for patiens with liver diseases, especially hepatitis induced by billiary obstruction due to decreased absorption and storage of vitamin A.
Treat and prevent deficiency of vitamin A, D in cases: nutritional rickets or osteomalacia, vitamin D-dependent rickets, familial hypophosphatemia (vitamin D-resistant rickets), rickets and osteomalacia due to anti-epileptic drugs; ocular dryness, nyctalopia; osteomalacia and osteoporosis; osteomalacia due to corticosteroids; renal osteodystrophy or secondary calcemia due to chronic kidney disease; hypoparathyroidism and pseudo- hypoparathyroidism. Prevent risk of falling and bone fractures in the elderly.
Supportively treat: Darier disease (Keratosis flollicularis), ichthyosis, abrasions, acne, psoriasis, mild lupus, rheumatoid arthritis; primary biliary cirrhosis or chronic cholestatic liver disease.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
– Prevention dosage:
Adults and children 12 years of age and above: take orally 1 soft-gel daily.
Children under 12 years of age: as directed by a physician.
– For treatment of diseases: as directed by a physician.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Patients with excessive vitamin A, hypercalcemia, vitamin D intoxication.
Pregnant women and lactating women (because the dose of Vitamin A exceeds the daily requirement for pregnant women and lactating women).
People with hypersensitivity to any ingredient of the medicine.
PRECAUTIONS:
Be cautious when combining with drugs that have vitamin A, D.
Be cautious in patients with sarcoidosis or hypoparathyroidism (may cause increased sensitivity to vitamin D); impairment of kidney function; heart disease; kidney stones; atherosclerosis.
PREGNANT WOMEN AND LACTATING WOMEN:
Vitamin A 5000 IU is higher than the daily requirement for pregnant women (2500 – 2567 IU) and lactating women (4000 – 4333 IU), so:
– Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant: not taken.
– Lactating women: not recommended because the risks of high dose have not been studied.
DRIVING AND OPERATING MACHINE ABILITY:
No effect.
UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS:
Side effects and adverse effects of vitamin A, D poisoning will occur with long-term high-dose vitamin AD (such as Vitamin D dosage ≥ 50,000 IU / day in people with normal and normal sensitivity parathyroid function to Vitamin D) or when taking a very high dose of vitamin AD, or in humans increased response to the normal dosage of vitamin D (lead to calcium metabolism disorders). Stop taking medicine, treat symptom and treat supportively.
Inform the physician immediately if any undesirable effect occurs while using the medicine.
DRUGS INTERACTIONS:
The following drugs should not be used concurrently with vitamin AD:
– Neomycin, liquid paraffin, cholestyramine, colestipol hydrochloride, mineral oil (when overuse): reduces the absorption of vitamin A, D in the intestine.
– Contraceptive pills: Increase plasma vitamin A levels and have an unfavorable effect on conception after stopping the contraceptive pill.
– Isotretinoin: Can lead to conditions like the vitamin A overdose.
– Phenobarbital, phenytoin: induces liver enzymes, increases the metabolism of vitamin D into inactive substances.
– Corticosteroid, rifampicin or isoniazid: reduces the effect of vitamin D.
– Thiazide diuretic, cardiac glycosides: can lead to hypercalcemia, lead to arrhythmias.
– Orlistat: can reduce the absorption of vitamin A, can cause low plasma vitamin A levels in some people.
– Warfarin: High dose of vitamin A may increase the effect of warfarin in decreasing blood prothrombin.
OVERDOSE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSE:
Chronic poisoning: When taking high dose of vitamin A for a long time.
Characteristic symptoms: fatigue, irritability, anorexia, weight loss, vomiting, digestive disorders, fever, enlarged liver and spleen, skin change, hair loss, dry hair, chapped and bleeding lips, anemia, headache, high blood calcium, subcutaneous edema, pain in the bone and joint. In children, symptoms of chronic poisoning include increased intracranial pressure (fontanelle tension), papilledema, tinnitus, visual disturbances, swell and pain along the long bones ( When you stop taking vitamin A, the symptoms also go away, but the bone can stop growing because of the long bones had started too early ossification).
Acute poisoning: when taking very high doses of vitamin A.
Characteristic signs: drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, irritability, headache, delirium and convulsions, diarrhea …. Symptoms appear after taking 6 to 24 hours.
Treatment: Stop taking the drug, treat symptom and treat supportively.
Vitamin D overdose:
Common early signs and symptoms of vitamin D poisoning are signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia such as weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, headache; anorexia, dry mouth, metallic taste, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramp, constipation, diarrhea, dizziness; Tinnitus, ataxia, rash, hypotonia, muscle pain, bone pain, and irritability.
Treatment: Stop taking the drug, stop taking calcium supplements, maintain low calcium diet, drink plenty of water or infuse fluids.
If necessary, corticosteroids or other drugs, particularly diuretics that increase calcium excretion (such as furosemide and ethacrynic acid) may be used to reduce serum calcium levels. Can use artificial kidney dialysis or peritoneal dialysis to remove free calcium from the body. If you have acute vitamin D poisoning when you have just drunk, it may be possible to prevent further absorption of vitamin D by vomiting or gastric lavage. If the drug is gone through the stomach, treatment with mineral oil can promote excretion of vitamin D in the feces.
DOSAGE FORM AND PRESENTATION:
Softgels. Box of 4 blisters of 10 softgels.
SHELF LIFE:
36 months from manufacturing date.
STORAGE:
In a cool (but not freezing) and dry place, temperature below 30°C, in an airtight container, protected from light and air.
SPECIFICATION:
Manufacturer’s.
MANUFACTURER RESPONSIBLE FOR THE GOODS:
OPC Pharmaceutical Joint Stock Company (1017 Hong Bang, Ward 12, District 6, Ho Chi Minh City).
MADE IN VIETNAM.